A qualitative dissertation involves using a particular approach to the research process, which includes crafting research questions, developing theories, and establishing a research strategy. It also requires presenting and discussing findings in a specific manner.
Here are some tips for writing a qualitative dissertation:
- Adopt a Qualitative Mindset: Shift your approach from quantitative to qualitative.
- Reflect on Your Role: Think about your involvement in the research project.
- Incorporate Theory: Consider the theoretical framework relevant to your research.
- Prioritize Depth: Focus more on depth of analysis rather than breadth.
- Integrate Processes: Aim to blend data collection, analysis, and writing.
- Move Beyond Description: Go further than just describing the data.
- Use Qualitative Writing: This style differs from quantitative writing, possibly using third-person or passive voice, addressing literature gaps in the introduction, and separating results from discussion.
- Combine Methods: Employ qualitative methods to formulate quantitative research questions or to interpret quantitative results, which can enrich your analysis or open new research avenues.
Steps to complete a qualitative dissertation:
- Choose a Specific Research Question: Develop a focused and precise research question.
- Select an Appropriate Design: Pick a suitable research design, such as a case study, ethnography, or grounded theory.
- Choose a Data Collection Method: Opt for methods like interviews, focus groups, observations, or content analysis.
- Collect and Analyze Data: Gather and analyze data according to your chosen method.
Understanding Qualitative Research

Understanding Qualitative Research involves recognizing its focus on exploring complex human experiences, behaviors, and social contexts. It prioritizes depth over breadth, using methods like interviews and observations and it seeks to understand the “why” and “how” behind phenomena, offering rich, interpretative insights into people’s lives and interactions.
Key Components of a Qualitative Research Dissertation
- Introduction in Qualitative Research Dissertation
- Research Problem and Questions: The introduction should clearly define the dissertation research problem and outline the dissertation research questions. These questions should be open-ended and exploratory, aiming to uncover deeper insights into the subject matter.
- Purpose and Significance: Explain the purpose of the study and its significance. This section should address why the dissertation research is important and how it contributes to the existing body of knowledge.
2. Literature Review
- Contextual Background: Provide a comprehensive review of the existing literature related to your dissertation research topic. This should include key theories, concepts, and previous studies.
- Theoretical Framework: Outline the theoretical framework guiding your study. This framework provides the lens through which you interpret your data and findings.
- Key Studies: Summarize key studies related to your dissertation research topic. Highlight gaps in the existing literature that your study aims to fill.
3. Methodology in Qualitative Research Dissertation
- Research Design: Describe the qualitative research design you have chosen, such as case studies, ethnography, or grounded theory. Explain why this design is appropriate for your research questions.
- Data Collection Methods: Detail the methods used to collect data, such as interviews, focus groups, participant observation, or document analysis. Discuss how these methods are suited to your research objectives.

- Sampling: Describe your sampling strategy, including how participants were selected and the criteria for inclusion. In qualitative research, this often involves purposive or theoretical sampling.
- Ethical Considerations: Address ethical issues related to your dissertation research, such as informed consent, confidentiality, and the handling of sensitive information.
4. Data Analysis
- Coding and Interpretation: Discuss the process of coding your data and identifying themes or patterns. This section should include how you ensure the rigor and validity of your analysis.
5. Findings
- Presentation of Results: Present the findings of your dissertation research in a clear and organized manner. Use direct quotes and examples from your data to illustrate key themes and insights.
- Interpretation: Interpret the findings in relation to your dissertation research questions and theoretical framework. Discuss how your results contribute to the understanding of the research problem.
6. Discussion
The discussion section interprets and contextualizes your findings. It should:
- Interpret Results: Provide an in-depth analysis of your findings, explaining their significance and implications. Discuss how your results align with or challenge existing theories and research.
- Discuss Implications: Explore the practical or theoretical implications of your findings. Consider how your research contributes to the field and its potential impact on practice or policy.
- Acknowledge Limitations: Recognize any limitations in your study, such as sample size, methodological constraints, or potential biases. Discuss how these limitations might affect your findings and suggest areas for future research.
7. Conclusion
- Summary of Findings: Summarize the key findings of your study. Reflect on the research questions and how they were addressed.
- Limitations: Acknowledge the limitations of your dissertation research, including any constraints related to methodology, data collection, or analysis.
- Recommendations: Offer recommendations based on your findings. These could be practical suggestions for practitioners or directions for future research.
8. References
Citing Sources: Provide a comprehensive list of references cited throughout your dissertation. Ensure that you follow the appropriate citation style for your field of study.
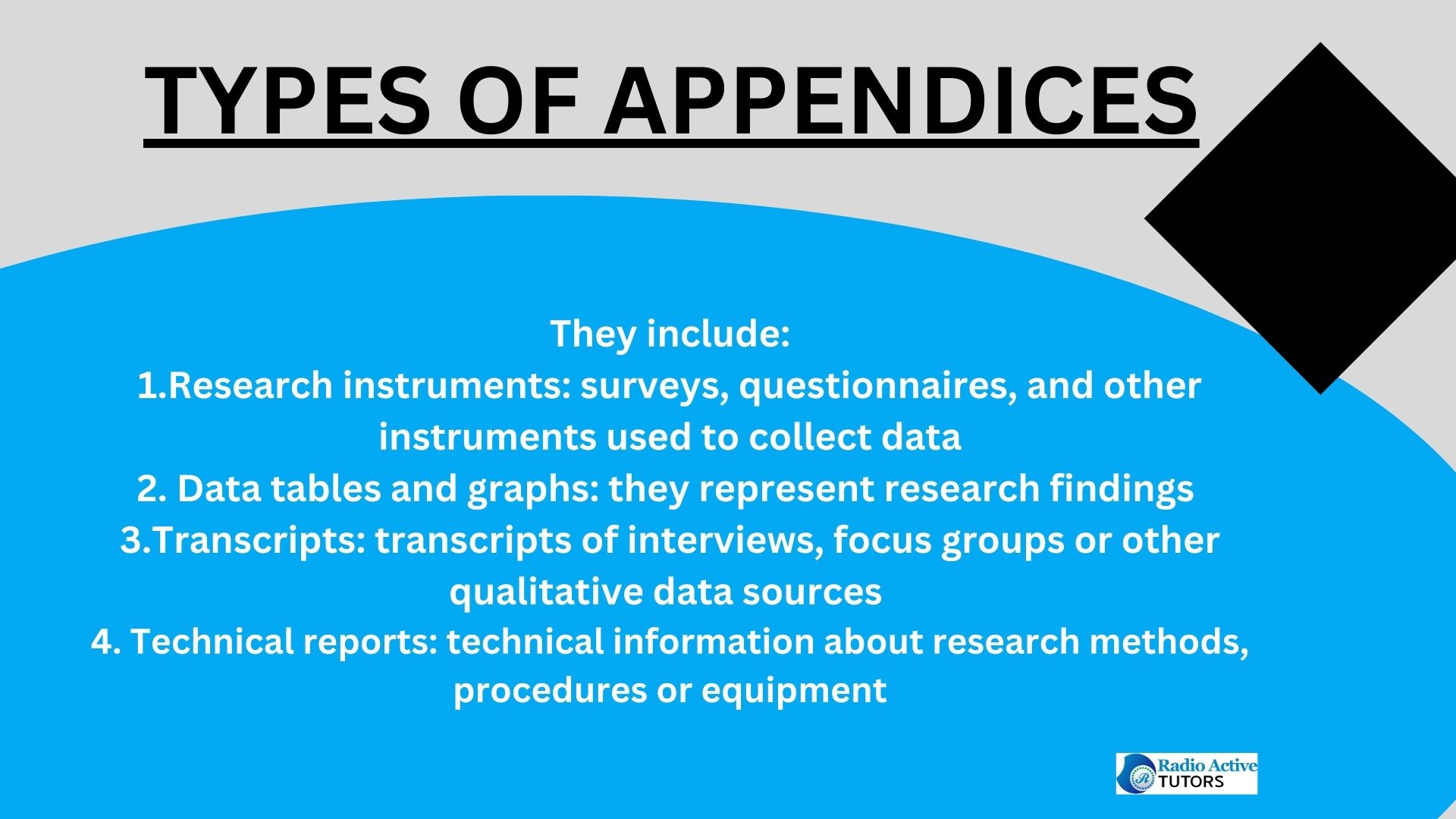
9. Appendices in Qualitative Research Dissertation
- Supplementary Material: Include any supplementary material. These appendices support the main text and provide transparency in your research process.
Methodological Considerations in Qualitative Research Dissertation
Qualitative research requires careful consideration of various methodological aspects:
- Researcher Bias: Reflect on your own biases and how they might influence the research process. It is essential to maintain reflexivity and be aware of how your perspectives shape the research.
- Trustworthiness and Rigor: Ensure the credibility, transferability, dependability, and confirmability of your research. Employ strategies such as member checking, triangulation, and peer debriefing to enhance the rigor of your study.
- Ethical Issues: Address any ethical concerns that arise during your research. Maintaining ethical standards is crucial for ensuring the integrity and respectfulness of your research.
Through careful design, data collection, and analysis, a qualitative dissertation offers a nuanced perspective on the research problem, advancing knowledge and informing practice in the field.
